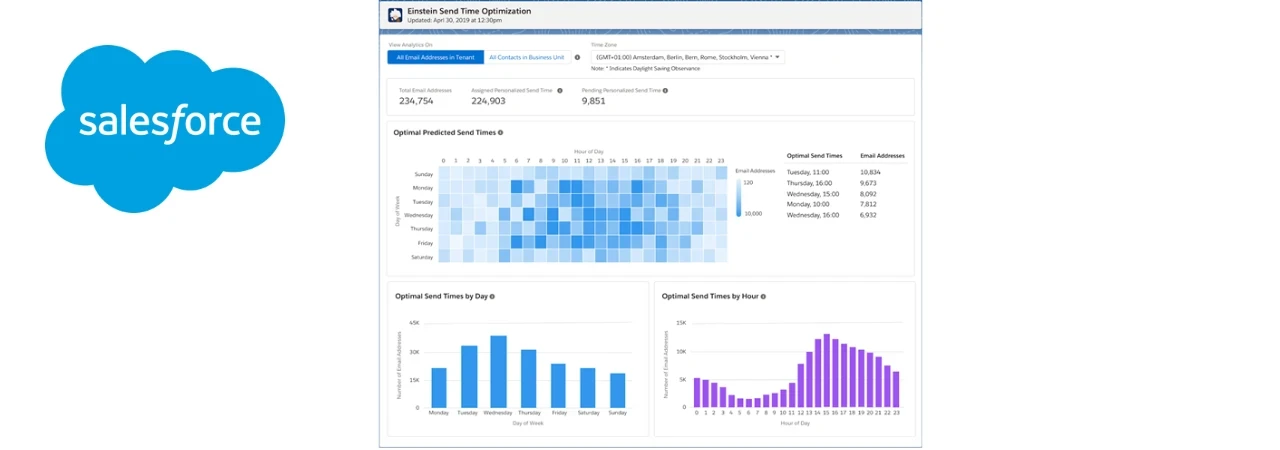
Marketing Cloud’s Einstein Send Time Optimization (STO) uses machine learning and 90 days of email engagement data to determine the best time within the next 24 hours to send a message to each contact. Include the Send Time Optimization activity on a journey immediately before an email activity to reach contacts when they are most likely to engage.
Einstein Send Time Optimization helps marketers increase Email Engagement. Using automated analysis, Einstein determines the best time to send an email to each individual contact. The Einstein STO Journey Builder activity can send email to each subscriber at the time when that subscriber is most likely to open the message. The Einstein Send Time Optimization application displays analytics that predicts future message engagement.
How send time optimization works?
Einstein gathers data for approximately 20 factors, such as the number of emails sent to a contact, the number of emails a contact opened, and the day of the week the email is opened. It uses machine learning to assign a weight to each factor according to that factor’s influence on predicting future engagement behavior. Then Einstein analyses this data and assigns a likelihood score to each of the 168 hours in a week for each contact. Send Time Optimization uses this information to recommend send times that lead to email opens.
This feature is available to customers with Marketing Cloud Einstein terms for Corporate, Enterprise, or Pro edition accounts with the Journey Builder add-on. To use this activity, activate Einstein Send Time Optimization for your business unit.
Optimize the send time of each message in a journey:
To increase overall engagement for a journey, add the Einstein Send Time Optimization (STO) activity before each email activity. Because the STO activity assigns the best hour to send based on individualized analysis, each message is sent to each contact in the journey at the hour within the next 24 hours that when the contact is most likely to open it.
For example, a marketer named Alex sets up a journey with one email message containing a coupon offer for new customers. When customers make an online purchase and opt in to receive offers from Alex’s company, completing the transaction enters each customer in Alex’s journey.
The first customer enters the journey Monday evening at 8:34 PM after purchasing and opting in. Einstein Send Time Optimization’s analysis determines that the customer is most likely to engage with email messages from 4:00-4:59 PM. So the journey sends this customer Alex’s coupon offer email at 4:00 PM on Tuesday, the day after the customer opted in.
A second customer enters the journey at 10:07 PM on Monday night. Einstein STO determines that the customer is most likely to engage with email messages from 10:00-10:59 PM. Because the customer reached the activity during the same hour Einstein identifies as best for sending, Einstein chooses the next best hour to send to this customer. STO analysis shows the next best hour as 7:00 AM. Thus, the journey sends the coupon to this customer at 7:00 AM on Tuesday morning.
A third customer enters the journey at 10:12 PM on Monday night. Einstein STO analysis shows that this customer is most likely to engage with email messages from 11:00-11:59 PM. So the journey sends the coupon offer to this customer at 11:00 PM the same night. Einstein does not send the message at 11:12 PM–exactly one hour after the contact entered the journey–because Einstein STO sends always occur at the beginning of the best scoring hour for each customer.
Add a random split activity to measure impact:
To measure the impact of send-time optimization, add the Einstein Send Time Optimization (STO) activity after a random split activity on a journey. Direct half the contacts in the journey to a path where a wait activity precedes the email activity. Direct the other half to a branch where the Einstein STO activity precedes the email activity. Then check the open rate for each email activity and compare them. Send more contacts down the Einstein-optimized path in your next journey, or in a subsequent version of this journey.
Combine with a wait activity:
To optimize send times when there is a minimum one-day wait between email messages in a customer journey, combine a wait activity and the Einstein STO activity.
Northern Trails Outfitters (NTO) marketing manager, Lisa, wants to optimize customer engagement for a welcome campaign. After customers subscribe to the NTO newsletter, they receive a series of three emails that set expectations and highlight the benefits of subscribing.
Before the second and third messages, she’s included a wait activity that instructs the system to wait two days before sending the next message. To ensure that an email is sent to each subscriber when that subscriber is most likely to open it, Lisa adds the Einstein STO activity between the wait activity and email activity for the second and third messages.
A customer named Alice and a customer named Bjorn both subscribes to the newsletter on a Tuesday. They each receive the initial welcome message within a few minutes. Remember, the journey doesn’t include an Einstein STO activity before this message, so the message sends when Alice and Bjorn reach the first email activity on the journey.
The second message is scheduled to send on Thursday. Based on Alice’s individual subscriber engagement behavior over the past 90 days, the journey sends the second message to Alice at 11:00 AM. Based on Bjorn’s engagement history, the journey sends the message to Bjorn at 7:00 PM.